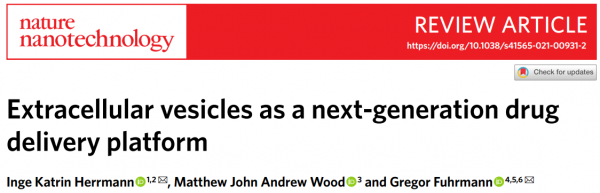
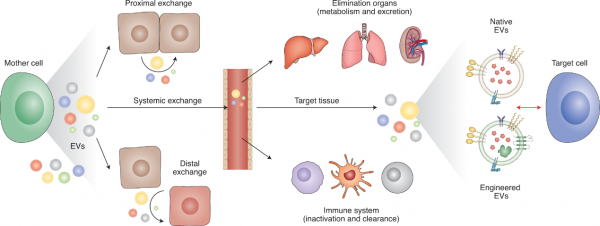
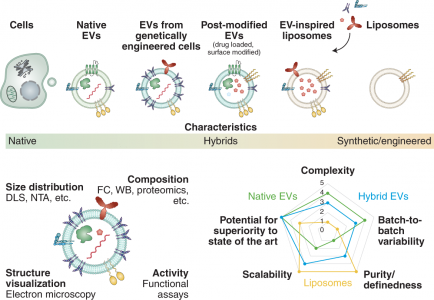
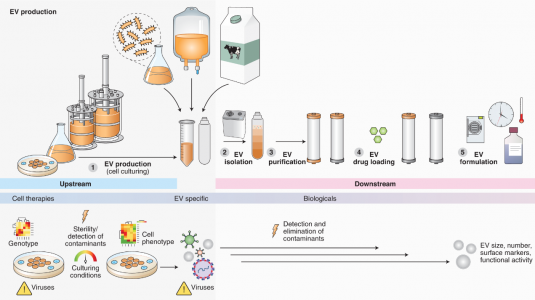
| No. | 试验名称 | 状态 | 适应症 | EV的类型 | 坐标 | NCT号 |
| Stem-cell-derived EVs |
| 1 | A Clinical Study of Mesenchymal Progenitor Cell Exosomes Nebulizer for the Treatment of Pulmonary Infections | Recruiting; phase 1/2 | Drug-resistant infections | MSC-/progenitor-cell-derived exosomes | Shanghai, China | NCT04544215 |
| 2 | Effect of Microvesicles and Exosomes Therapy on β-Cell Mass in Type I Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) | Unknown status | Diabetes mellitus type 1 | MSC-derived exosomes | Sahel, Egypt | NCT02138331 |
| 3 | Evaluation of Safety and Efficiency of Exosome Inhalation in SARS-CoV-2 Associated Pneumonia | Enrolling by invitation; phase 1/2 | SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia | MSC-derived exosomes | Samara, Russia | NCT04491240 |
| 4 | A Pilot Clinical Study on Inhalation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exosomes for the Treatment of Severe Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia | Completed; phase 1 | SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia | MSC-derived exosomes | Shanghai, China | NCT04276987 |
| 5 | Safety and Efficiency of Method of Exosome Inhalation in COVID-19 Associated Pneumonia | Enrolling by invitation; phase 2 | SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia | MSC-derived exosomes | Samara, Russia | NCT04602442 |
| 6 | Effect of UMSCs Derived Exosomes on Dry Eye in Patients With cGVHD | Recruiting; phase 1/2 | Dry eye | Umbilical MSC-derived exosomes | Guangzhou, China | NCT04213248 |
| 7 | MSC-Exos Promote Healing of MHs | Recruiting; early phase 1 | Macular holes | MSC-derived exosomes | Tianjin, China | NCT03437759 |
| 8 | A Tolerance Clinical Study on Aerosol Inhalation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exosomes in Healthy Volunteers | Recruiting; phase 1 | Safety and tolerance studies | MSC-derived exosomes | Shanghai, China | NCT04313647 |
| 9 | Allogenic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosome in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke | Completed; phase 1/2 | Cerebrovascular disorders | Mesenchymal-stromal-cell-derived exosomes | Tehran, Iran | NCT03384433 |
| 10 | Evaluation of Adipose Derived Stem Cells Exosomes in Treatment of Periodontitis | Recruiting; early phase 1 | Periodontitis | Adipose-derived stem-cell-derived exosomes | Cairo, Egypt | NCT04270006 |
| Allogenic and autologous EVs | | | | | |
| 11 | Safety and Efficacy Evaluation of Allogenic Adipose MSC-Exosomes in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease | Recruiting; phase 1/2 | Alzheimer’s disease | Allogenic adipose MSC-derived exosomes | Shanghai, China | NCT04388982 |
| 12 | A Clinical Study of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Nebulizer for the Treatment of ARDS | Not yet recruiting; phase 1/2 | Acute respiratory distress syndrome | Allogeneic human MSC-derived exosomes | Ruijin, China | NCT04602104 |
| 13 | MSC Extracellular Vesicles in Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa | Not yet recruiting; phase 1 | Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa | Allogeneic MSC-derived EVs | Aegle Therapeutics | NCT04173650 |
| 14 | Effect of Plasma Derived Exosomes on Cutaneous Wound Healing | Enrolling by invitation; early phase 1 | Ulcer | Autologous exosome-rich plasma | Kumamoto, Japan | NCT02565264 |
| Other cells or EV sources | | | | | |
| 15 | COVID-19 Specific T Cell Derived Exosomes | Active; phase 1 | SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia | T-cell-derived exosomes | Kayseri, Turkey | NCT04389385 |
| 16 | Extracellular Vesicle Infusion Therapy for Severe COVID-19 | Not yet recruiting; phase 2 | SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome | Bone-marrow-derived EVs | Direct Biologics | NCT04493242 |
| 17 | Edible Plant Exosome Ability to Prevent Oral Mucositis Associated with Chemoradiation Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer | Active; phase 1 | Head and neck cancer, oral mucositis | Grape exosomes and fentanyl patch | Louisville, USA | NCT01668849 |
| Drug-loaded EVs | | | | | |
| 18 | iExosomes in Treating Participants with Metastatic Pancreas Cancer with KrasG12D Mutation | Recruiting; phase 1 | Metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | Mesenchymal-stromal-cell-derived exosomes loaded with siRNA against KrasG12D | Houston, USA | NCT03608631 |
| 19 | Study Investigating the Ability of Plant Exosomes to Deliver Curcumin to Normal and Colon Cancer Tissue | Active; phase 1 | Colon cancer | Plant exosomes loaded with curcumin | Louisville, USA | NCT01294072 |
| 20 | Trial of a Vaccination with Tumor Antigen-loaded Dendritic Cell-derived Exosomes | Completed; phase 2 | Non-small-cell lung cancer | Dendritic-cell-derived exosomes loaded with antigen | Villejuif, France | NCT01159288 |